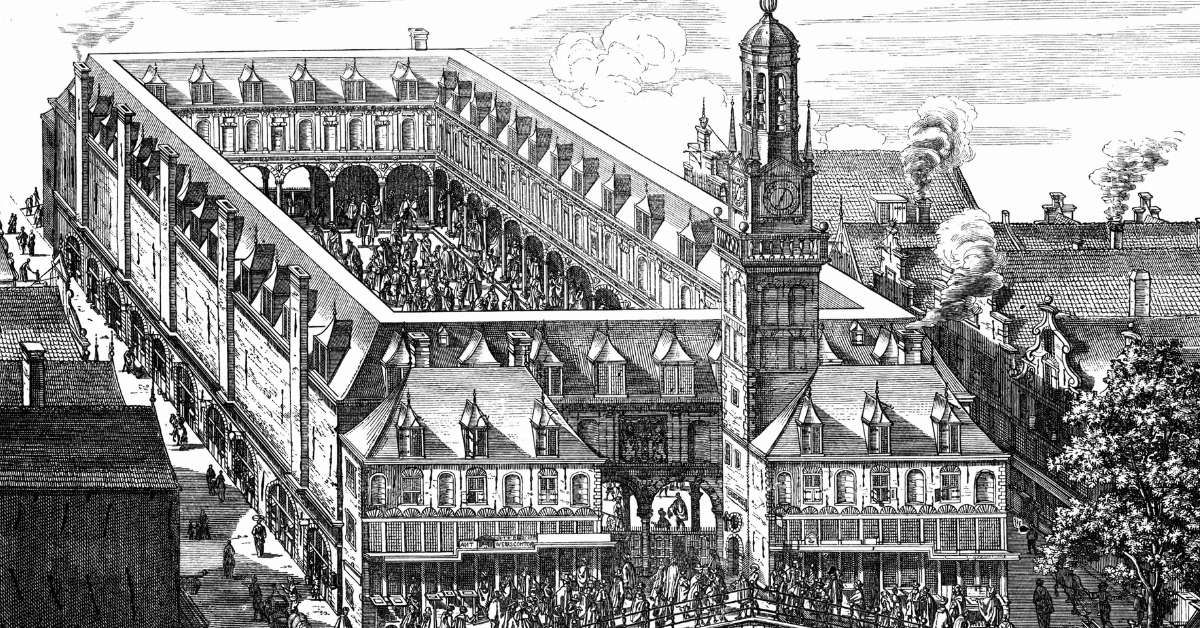
The Amsterdam Stock Exchange, founded in 1602, is often hailed as the world’s first official stock exchange—the very institution that laid the foundation for today’s modern stock markets. It was created during the Dutch Golden Age, a time when the Netherlands emerged as a global trading powerhouse, and it all began with a visionary idea by the Dutch East India Company (VOC).
In need of funds for their vast trade expeditions, the VOC did something revolutionary—they issued tradable shares to the public, allowing ordinary citizens to invest in the company and share in its profits. This opened up a whole new way of financing large enterprises, making it possible for people to buy and sell ownership stakes for the first time in history!
Initially, stock trading wasn’t formalized—it happened in local coffee houses, where merchants haggled over prices. But soon, as trading gained popularity, the Amsterdam Stock Exchange moved into its very own building, the Beurs van Hendrick de Keyser in 1611, creating a dedicated, regulated space for transactions.
The exchange’s strict rules, like standardized trading hours and a ban on insider trading, helped build trust and ensured fair practices. Fast forward to today, the Amsterdam Stock Exchange is part of Euronext and continues to be a major global financial hub.
Interestingly, governments also joined in—Austria led the way in 1695 by issuing the first government bonds on the Amsterdam Exchange. Soon after, other European nations followed, transforming the exchange into not just a trading hub but a pioneering platform that laid the foundation for the global financial markets we know today.